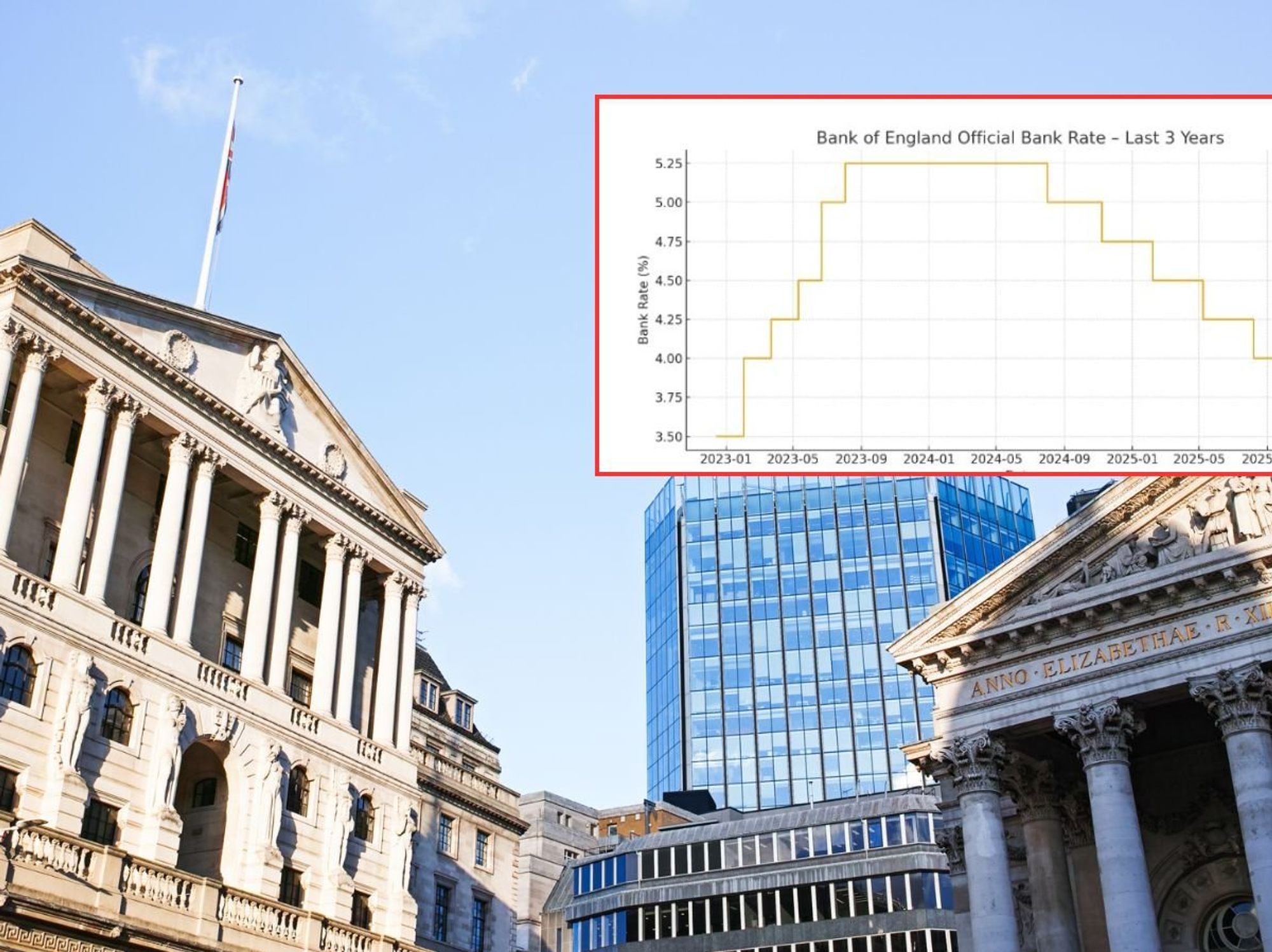
Covid: First at-home pill to treat coronavirus approved in the UK
Undated handout photo released by Merck & Co Inc and obtained by Reuters May 17, 2021. | MERCK & CO INC
Drug prevents virus from multiplying, therefore reducing the severity of the disease
Don't Miss
Most Read
The first anti-viral pill for Covid-19 that can be taken at home has been approved for use in the UK.
Molnupiravir is for people who have had a positive Covid test and have at least one risk factor for developing severe illness, such as obesity, being over the age of 60, diabetes or heart disease.
The UK’s Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency (MHRA) said the drug is safe and effective at reducing the risk of hospital admission and death in people with mild to moderate Covid who are at extra risk from the virus.
The drug, from Ridgeback Biotherapeutics and Merck Sharp & Dohme (MSD), works by interfering with the virus’s replication.
It prevents the virus from multiplying, keeping levels low in the body and therefore reducing the severity of the disease.
The MHRA said the drug should be taken as soon as possible following a positive Covid-19 test and within the first five days.
The Government announced last month that it had secured 480,000 courses of molnupiravir after a study found it cut the rate of hospital admission and death by 50% in mild-to-moderately ill patients who had at least one risk factor for the disease.
In the study, the tablet was given twice a day to patients recently diagnosed with coronavirus.
Health and Social Care Secretary, Sajid Javid, said: “Today is a historic day for our country, as the UK is now the first country in the world to approve an anti-viral that can be taken at home for Covid-19.
“This will be a gamechanger for the most vulnerable and the immunosuppressed, who will soon be able to receive the ground-breaking treatment.
“We are working at pace across the Government and with the NHS to set out plans to deploy molnupiravir to patients through a national study as soon as possible
“This antiviral will be an excellent addition to our armoury against Covid-19, and it remains vital everyone comes forward for their life-saving Covid-19 vaccine – particularly those eligible for a booster – to ensure as many people as possible are protected over the coming months.”
Dr June Raine, MHRA chief executive, said: “Following a rigorous review of the data by our expert scientists and clinicians, we are satisfied that Lagevrio (molnupiravir) is safe and effective for those at risk of developing severe Covid-19 disease and have granted its approval.
“Lagevrio is another therapeutic to add to our armoury against Covid-19.
“It is also the world’s first approved anti-viral for this disease that can be taken by mouth rather than administered intravenously.
“This is important, because it means it can be administered outside of a hospital setting, before Covid-19 has progressed to a severe stage.
“With no compromises on quality, safety and effectiveness, the public can trust that the MHRA has conducted a robust and thorough assessment of the data.”
It comes as data from the Office for National Statistics (ONS) found an estimated 1.2 million people in private households in the UK reported experiencing long Covid in the four weeks to October 2.
This is up from 1.1 million a month earlier and reflects “sustained increased Covid-19 infection rates in August,” the ONS said.
Of the 1.2 million, an estimated 849,000 first had Covid-19 – or suspected they had Covid-19 – at least 12 weeks previously, while 426,000 first had the virus or suspected they had the virus at least one year ago.
Prevalence of self-reported long Covid was “notably higher” among people aged 12 to 16 or 17 to 24, compared with the previous month, the ONS found.
An estimated 1.3% of 12 to 16-year-olds experienced long Covid in the four weeks to October 2, the equivalent of 49,000 people – up from 0.9% (35,000 people) in the four weeks to September 5.
The figure for 17 to 24-year-olds was 2.4% (142,000), up from 1.9% (112,000).
Long Covid was estimated to be adversely affecting the day-to-day activities of 780,000 people – around two-thirds of those with self-reported long Covid – with 233,000 reporting that their ability to undertake day-to-day activities had been “limited a lot”.
Fatigue continued to be the most common symptom (experienced by 55% of those with self-reported long Covid), followed by shortness of breath (39%), loss of smell (33%) and difficulty concentrating (30%).