Elon Musk accidently punches hole in atmosphere after rocket explodes in mid-air
Elon Musk's rocket exploded shortly after its launch in Texas
|GB News

The explosion was so intense it ripped through the ionosphere, the electrically charged layer of the atmosphere that plays a key role in radio communication and satellite signals
Don't Miss
Most Read
When SpaceX launched its massive Starship rocket for just the second time in November 2023, it didn't just break records—it broke the sky.
Scientists have recently revealed that the raw power of the launch punched a temporary hole through the upper atmosphere, creating a phenomenon never seen before.
The rocket's booster separated as planned, but four minutes later it exploded mid-air.
Starship itself then detonated about 93 miles above Earth shortly after.
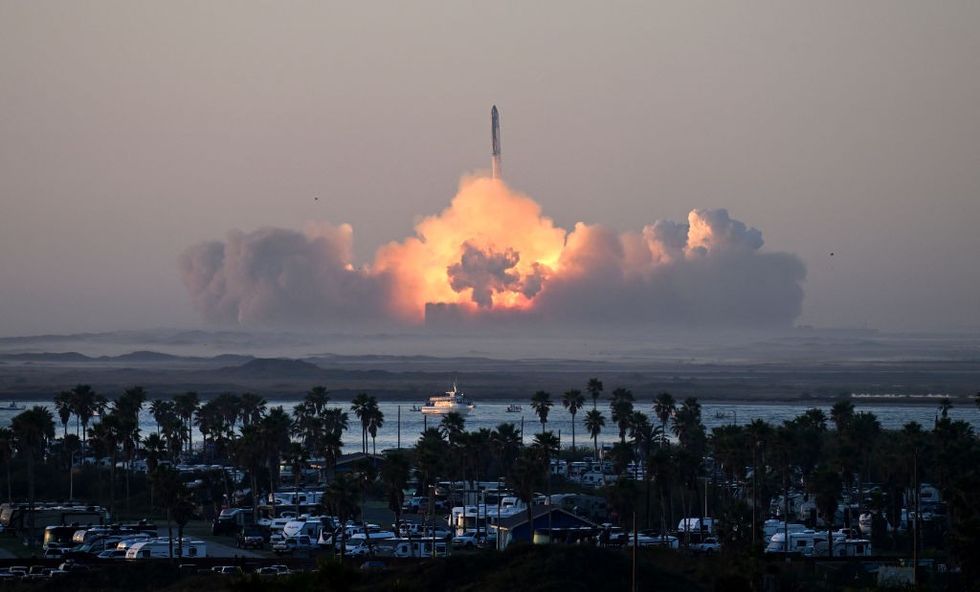

The rocket's booster separated as planned, but four minutes later it exploded mid-air
|Getty
The second explosion was so intense it ripped through the ionosphere, the electrically charged layer of the atmosphere that plays a key role in radio communication and satellite signals.
According to researchers, this is the first time a hole in the ionosphere has been caused by a catastrophic event like a rocket explosion.
"Usually, such holes form due to chemical reactions from engine fuel," explained Yury Yasyukevich, lead researcher and ionosphere physicist at the Russian Academy of Sciences' Institute of Solar-Terrestrial Physics.
"But this time, it was caused by the sheer shock wave from the Starship explosion."
LATEST DEVELOPMENTS:
 Space X's next generation Starship | Reuterws
Space X's next generation Starship | ReuterwsUsing data from satellites and ground observatories, scientists observed the gaping hole remain open for 30 to 40 minutes before the ionosphere naturally stitched itself back together.
Yasyukevich's research team used data from ground-based Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) receivers to investigate how the Starship explosion affected the ionosphere.
Their analysis revealed that when Starship exploded, the resulting shock wave scattered free electrons, temporarily disrupting the plasma and creating a "hole" where the ionosphere's usual properties were depleted.
The researchers published their study in the journal Geophysical Research Letters in August 2024.
"Analysing the data and understanding their nature, we understand more deeply the structure of the ionosphere, [and] the nature of the phenomena that occur in it," Yasyukevich told TASS, a Russian news agency.

Elon Musk founded SpaceX in 2002
|Reuters
This novel event offered scientists a rare opportunity to learn more about this atmospheric layer.
Since that inaugural flight, Starship has been launched seven more times for a total of eight test flights. Four of them have been explosive failures.
SpaceX has yet to successfully launch Starship in 2025.
Flights seven and eight saw the booster successfully return to Starbase, but the upper stage exploded 10 minutes after lift off during both flights.
SpaceX is currently preparing for the rocket's ninth test flight, scheduled for May 20.










